Change Your Voice: Change Your Life: A Quick, Simple Plan for Finding & Using Your Natural Dynamic Voice Morton Cooper on Amazon.com.FREE. shipping on qualifying offers. In addition to the social distancing changes, the set also looked slightly different. Because of the hiatus I Can See Your Voice was forced to take due to the coronavirus, the producers and set designers had some time to make additional changes to the set both to make up for the lack of audience, as well as to introduce some other COVID-19 safety protocols. Here are four common voice levels, excerpted from my book (click on title): 'How to Improve the Sound of Your Speaking Voice.' Most of us have heard someone with a nasal voice.
Change in voice
Voice change symptoms
- Abnormal changes in the voice are called 'hoarseness'
- When hoarse, the voice may sound breathy, raspy, strained, or show changes in volume or pitch
- Voice changes are related to disorders in the sound-producing parts (vocal folds) of the voice box (larynx)
- While breathing, the vocal folds remain apart
- When speaking or singing, they come together and, as air leaves the lungs, they vibrate, producing sound
- Swelling or lumps on the vocal folds hinder vibration, altering voice quality, volume, and pitch
What are the causes of a change in voice?
Acute Laryngitis
- The most common cause is acute laryngitis—swelling of the vocal folds that occur during a common cold, upper respiratory tract viral infection, or from voice strain
- Serious injury to the vocal folds can result from strenuous voice use during an episode of acute laryngitis
Voice Misuse
Voice Ganger

- Speaking in noisy situations
- Excessive use
- Telephone use with the handset cradled to the shoulder
- Using inappropriate pitch (too high or too low) when speaking
- Not using amplification when public speaking
Benign Vocal Cord Lesions
- Prolonged hoarseness can occur when you use your voice too much, or too loudly for extended periods of time
- These habits can lead to nodules, polyps, and cysts
- Vocal nodules (singers' nodules) are callus-like growths of the vocal folds
- Vocal fold polyps and cysts also occur in those who misuse their voice, but can also occur in those who do not
Vocal Haemorrhage
- If you experience a sudden loss of voice following a yell or other strenuous vocal use, you may have developed a vocal fold haemorrhage
- Vocal fold haemorrhage occurs when one of the blood vessels on the surface of the vocal folds ruptures and the soft tissues fill with blood
- It is considered a vocal emergency and should be treated with absolute voice rest and examination by an otolaryngologist (ear nose and throat doctor)
Gastro-oesophageal Reflux (GORD)
- A possible cause of hoarseness is gastro-oesophageal reflux, when stomach acid comes up the swallowing tube (oesophagus) and irritates the vocal folds
- Other typical symptoms of GORD include heartburn and regurgitation
- Usually, the voice is worse in the morning and improves during the day
- These people may have a sensation of a lump or mucus in their throat and have an excessive desire to clear it
Laryngo-pharyngeal Reflux (LPR)
- If the reflux effects the back of the throat, it is called LPR rather than GORD
- The structures in the throat (pharynx, larynx, and lungs) are much more sensitive to stomach acid and digestive enzymes, so smaller amounts of the reflux into this area can result in more damage
- Many patients with LPR do not have heartburn or other classic symptoms of GORD
Smoking
- Smoking is another cause of hoarseness
- Because smoking is the major cause of throat cancer, if smokers become hoarse, they should see an otolaryngologist
Neurological Diseases or Disorders
- Hoarseness can also appear in those who have neurological diseases such as Parkinson's or a stroke, or may be a symptom of spasmodic dysphonia, a rare neurological disorder that usually affects only the voice, but sometimes affects breathing
- A paralysed vocal fold may be the cause of a weak, breathy voice
- If the hoarseness persists for more than three months and other causes have been ruled out, a neurologist may be helpful for diagnosis
Other Causes for voice change
- These include allergies, thyroid problems, trauma to the voice box, and, occasionally, menstruation
- Very serious conditions such as laryngeal cancer can also cause hoarseness, which is why it is important to have chronic hoarseness evaluated promptly by an ENT specialist
How is voice change treated?
Hoarseness treatment
- Hoarseness caused by a cold or flu may be evaluated by family doctors, paediatricians, and physicians who have learned how to examine the larynx
- Problems with the voice are often best managed by a team of professionals who know and understand how the voice functions
- These professionals are ENT specialists, speech/language pathologists, and teachers of singing, acting, and public speaking
- Vocal nodules, polyps, and cysts are typically treated with a combination of microsurgery and voice therapy
How is voice change evaluated?
- An ENT specialist will obtain a thorough history of a patient's hoarseness and general health
- They will then evaluate the voice and do a complete ear, nose, and throat exam
- This includes examination of the vocal folds by laryngoscopy
- Laryngoscopy may be suggested by the ENT specialist at any time during an evaluation for hoarseness, but if it persists beyond three weeks it should be evaluated and that evaluation should occur within a maximum of 3 months
- The evaluation should be immediate if there is concern about a serious underlying cause is suspected
- Doctors usually look at the vocal folds either with a mirror placed in the back of the throat, or with a very small, lighted flexible tube (fiberoptic scope) that is passed through the nose to view the vocal folds
- Videotaping or stroboscopy (slow-motion assessment) may also help with the analysis
- These procedures are well tolerated by most patients
- In some cases, special tests designed to evaluate the voice may be recommended
- These measure voice irregularities, how the voice sounds, airflow, and other characteristics that are helpful in diagnosing and guiding treatment
How are vocal disorders treated?
- Speaking in noisy situations
- Excessive use
- Telephone use with the handset cradled to the shoulder
- Using inappropriate pitch (too high or too low) when speaking
- Not using amplification when public speaking
Benign Vocal Cord Lesions
- Prolonged hoarseness can occur when you use your voice too much, or too loudly for extended periods of time
- These habits can lead to nodules, polyps, and cysts
- Vocal nodules (singers' nodules) are callus-like growths of the vocal folds
- Vocal fold polyps and cysts also occur in those who misuse their voice, but can also occur in those who do not
Vocal Haemorrhage
- If you experience a sudden loss of voice following a yell or other strenuous vocal use, you may have developed a vocal fold haemorrhage
- Vocal fold haemorrhage occurs when one of the blood vessels on the surface of the vocal folds ruptures and the soft tissues fill with blood
- It is considered a vocal emergency and should be treated with absolute voice rest and examination by an otolaryngologist (ear nose and throat doctor)
Gastro-oesophageal Reflux (GORD)
- A possible cause of hoarseness is gastro-oesophageal reflux, when stomach acid comes up the swallowing tube (oesophagus) and irritates the vocal folds
- Other typical symptoms of GORD include heartburn and regurgitation
- Usually, the voice is worse in the morning and improves during the day
- These people may have a sensation of a lump or mucus in their throat and have an excessive desire to clear it
Laryngo-pharyngeal Reflux (LPR)
- If the reflux effects the back of the throat, it is called LPR rather than GORD
- The structures in the throat (pharynx, larynx, and lungs) are much more sensitive to stomach acid and digestive enzymes, so smaller amounts of the reflux into this area can result in more damage
- Many patients with LPR do not have heartburn or other classic symptoms of GORD
Smoking
- Smoking is another cause of hoarseness
- Because smoking is the major cause of throat cancer, if smokers become hoarse, they should see an otolaryngologist
Neurological Diseases or Disorders
- Hoarseness can also appear in those who have neurological diseases such as Parkinson's or a stroke, or may be a symptom of spasmodic dysphonia, a rare neurological disorder that usually affects only the voice, but sometimes affects breathing
- A paralysed vocal fold may be the cause of a weak, breathy voice
- If the hoarseness persists for more than three months and other causes have been ruled out, a neurologist may be helpful for diagnosis
Other Causes for voice change
- These include allergies, thyroid problems, trauma to the voice box, and, occasionally, menstruation
- Very serious conditions such as laryngeal cancer can also cause hoarseness, which is why it is important to have chronic hoarseness evaluated promptly by an ENT specialist
How is voice change treated?
Hoarseness treatment
- Hoarseness caused by a cold or flu may be evaluated by family doctors, paediatricians, and physicians who have learned how to examine the larynx
- Problems with the voice are often best managed by a team of professionals who know and understand how the voice functions
- These professionals are ENT specialists, speech/language pathologists, and teachers of singing, acting, and public speaking
- Vocal nodules, polyps, and cysts are typically treated with a combination of microsurgery and voice therapy
How is voice change evaluated?
- An ENT specialist will obtain a thorough history of a patient's hoarseness and general health
- They will then evaluate the voice and do a complete ear, nose, and throat exam
- This includes examination of the vocal folds by laryngoscopy
- Laryngoscopy may be suggested by the ENT specialist at any time during an evaluation for hoarseness, but if it persists beyond three weeks it should be evaluated and that evaluation should occur within a maximum of 3 months
- The evaluation should be immediate if there is concern about a serious underlying cause is suspected
- Doctors usually look at the vocal folds either with a mirror placed in the back of the throat, or with a very small, lighted flexible tube (fiberoptic scope) that is passed through the nose to view the vocal folds
- Videotaping or stroboscopy (slow-motion assessment) may also help with the analysis
- These procedures are well tolerated by most patients
- In some cases, special tests designed to evaluate the voice may be recommended
- These measure voice irregularities, how the voice sounds, airflow, and other characteristics that are helpful in diagnosing and guiding treatment
How are vocal disorders treated?
- The treatment of hoarseness depends on the cause
- Many common causes of hoarseness can be treated simply by resting the voice or modifying how it is used
- An ENT specialist may make some recommendations about voice use behaviour, refer the patient to other voice team members, and in some instances recommend surgery if a lesion, such as a polyp, is identified
- Not smoking and avoiding second hand smoke is recommended to all patients
- Drinking fluids and taking medications to thin out the mucus may help
How to prevent hoarseness
- Specialists in speech/language pathology (voice therapists) are trained to assist patients in behavior modification to help eliminate some voice disorders
- Patients who have developed bad habits, such as smoking or overusing their voice by yelling and screaming, benefit most from this conservative approach
- The speech/language pathologist may teach patients to alter their methods of speech production to improve the sound of the voice and to resolve problems, such as vocal nodules
- When a patient's problem is specifically related to singing, a singing teacher may help to improve the patients' singing techniques
Voice care – Hoarseness prevention tips
- If you smoke, quit
- Avoid agents that dehydrate the body, such as alcohol, caffeine and salt
- Avoid second hand smoke
- Stay hydrated—drink plenty of water
- Humidify your home
- Watch your diet—avoid spicy foods
- Try not to use your voice too long or too loudly
- Use a microphone if possible in situations where you need to project your voice
- Seek professional voice training
- Avoid speaking or singing when your voice is injured or hoarse
When should I see an ENT specialist?
- If hoarseness lasts longer than three weeks, especially if you smoke
- If you do not have a cold or flu
- If you are coughing up blood
- If you have difficulty swallowing
- If you feel a lump in the neck
- If you observe loss or severe changes in voice lasting longer than a few days
- If you experience pain when speaking or swallowing
- If difficulty breathing accompanies your voice change
- If your hoarseness interferes with your livelihood
- If you are a vocal performer and unable to perform
If you become hoarse frequently or notice voice change, contact your local doctor, who will arrange for you to see an ENT specialist.
Your vocal cords and other physiological factors determine the sound of your voice. Your adult voice sets well by the time you have surpassed puberty. Sometimes, some environmental factors may project your voice in a different way. Some techniques can help you make slight changes to your pitch and volume to bring out your natural voice in the best possible way, although, it is not possible to completely change your voice from high to low or from low to high.
How to Change Your Voice for Real
You can change your real voice by altering the place you pronounce, practicing certain pronouncing methods and imitating your favorite voices. Let's get closer to know more.
1. Shift the Place You Pronounce
People generally speak from the diaphragm, throat and nose. A good balance between them is necessary. Elder scrolls 5 skyrim review.
- Diaphragm: Diaphragm is a large band of muscle under your lungs and above the stomach. In order to speak from your diaphragm, first place a hand on your abdomen right below the ribs. As you take a breath to speak, your stomach should blow a little, but not your chest. If your vocal volume is less, then speaking from the diaphragm helps improve resonance.
- Throat: Learn to speak from your throat by pinching your nose and holding a sustained note. This improves your speech by relaxing your throat muscles. If you have a squeaky or screechy voice, relaxed vocal folds can deepen your voice. If you have a nasal speech, diverting the air from your sinuses to your throat helps a lot.
- Nose: How to change your voice? Speak from your nose. Practice inhaling through your mouth and exhaling through your nose. Take 4-5 breaths, hum a little and then speak, keeping your tongue shallow and mouth small. By reopening the nasal pathways, it helps with your stuffy speech which may be caused by a blocked nose during chronic sinus inflammation.
2. Use Some Techniques
Actors/singers learn to keep their voice in good condition because voice is their career. They have proven to us that many techniques do helps to change your voice.
- Lip Thrills: This technique helps you relax your vocal folds and close cords. To do this, blow air through gently closed lips. If you are doing it correctly, the lips should vibrate against each other. Slowly add long and short vowel sounds of various pitches.
- Nay-Nays: This is a very helpful nasal speech practice. For this, you have to pretend that you are taunting someone in a bratty voice by saying 'nay-nay'. A gentle buzz should be felt in your sinuses as you are practicing this.
- Ahhhs: This technique is for lowering the vocal pitch of those people who have high pitched or squeaky voices. Inhale deeply and exhale slowly saying 'ahhh'. Try to hold it for as long as you can.
- Oh-Ah-Oohs: How to change your voice? Inhaling and saying 'oh-ah-ooh again and again will do. Do a glottal stop and stress on the dipthong of every syllable. Do not pause for long periods. It is a little faster and energetic, and you will feel your vocal cords constrict or close a little.
3. Imitation Works
Apps That Alter Your Voice
If you like a particular voice, say that of some actor, try to imitate the voice. You should analyze the voice's pitch, tone, enunciation and cadence. Start the practice by trying to modify your voice to speak in the exact same way as your voice role model. Later you can just apply the parts of the voice you deem to be the best.
How to Disguise Your Voice
Voice Altering Devices
Apart from trying to change your real voice, you can also try to disguise it by using various techniques.
1. Muffle Your Voice
Your voice travels in the form of sound waves through different mediums. The same waves transmit through the air differently than those through any other medium like solids or liquids. So, to muffle your voice, place your hand, a handkerchief or other obstacles directly over your mouth as you speak to produce a more dramatic effect. By placing an obstacle in front of your mouth, you force the sound waves through that obstacle and thus change the way how others receive and interpret the sound. Cookie animal crossing new leaf.
2. Speak in Monotone
Use less emotion while speaking and your voice will sound different. For example, most people, when asking a question, end with a higher intonation. The same question sounds different when spoken in a flat tone. If people tell you that you have a flat voice, then practice speaking with more emotion or enthusiasm. Think carefully before speaking and change your intonation. Start practicing with simple phrases.
3. Hold Your Nose as You Speak
You can learn how to change your voice by holding your nose and blocking your nasal passages. This is a quick and dramatic way to do it. Just grasp your nose from both the sides and close the nostrils. When you speak, air flows naturally through your mouth and your nose. When you block your nose, the amount of air that would have escaped through your nasal passages is restricted and the air gets trapped deeper in your throat and mouth, thereby changing the pressure. This causes your vocal cords to vibrate in a different way and changes the way your voice sounds.
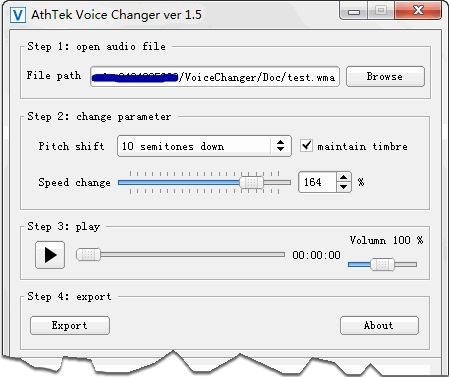
Software To Alter Voice
4. Use a Voice Changer
Voice changing devices are available online, costing anything from $25 to $50. Each device works differently so do check the specifications before you buy a device. Most devices are portable and have the ability to change the pitch of your voice in many ways. Read the instructions carefully and learn the right way to use the device. Some of the devices require a pre-recorded message while others can be used to adjust your voice as you speak, transmitting the altered sound through a cell phone or another speaker.

